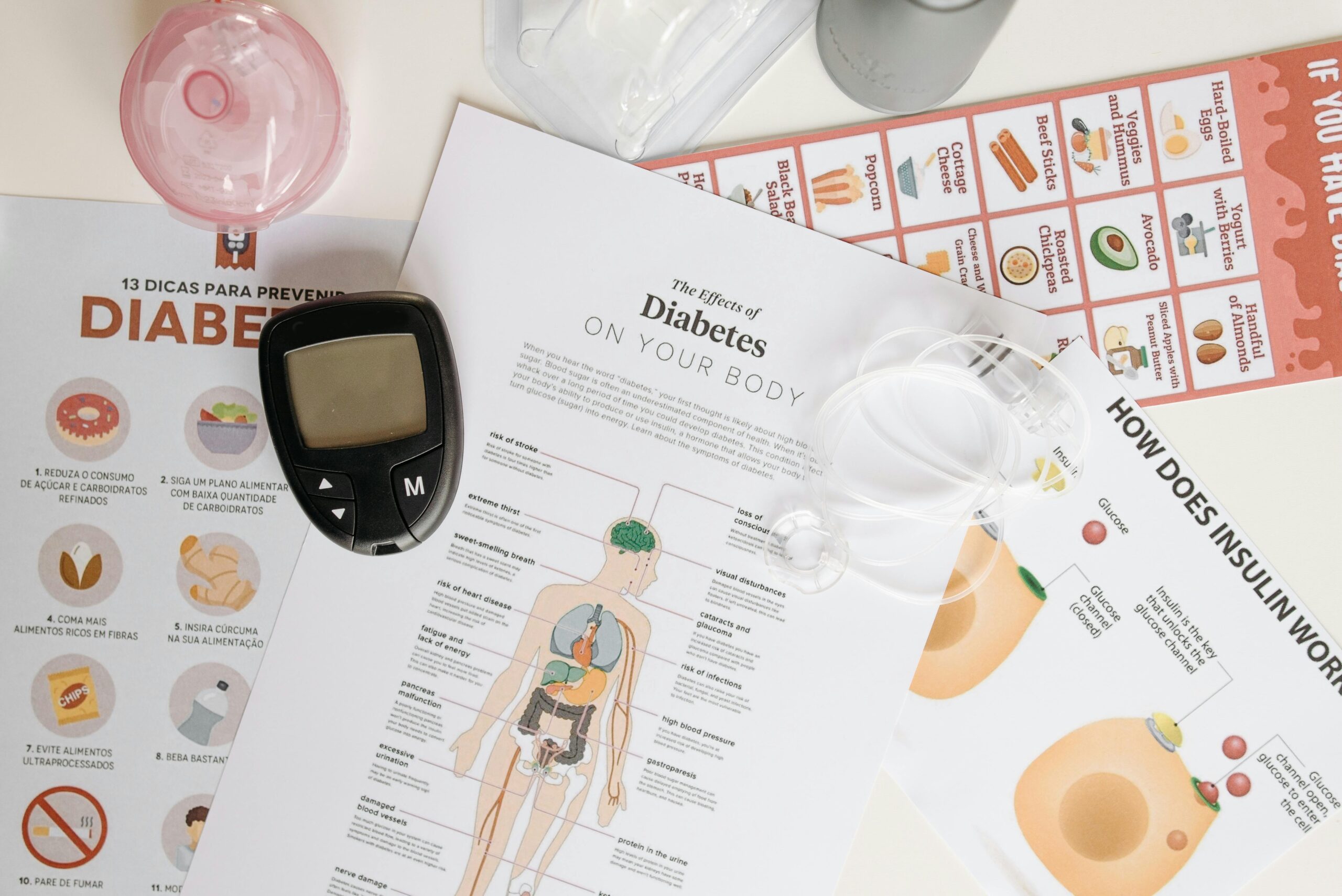
Chronic diseases are long-term health conditions that generally progress slowly and require ongoing management. These diseases are one of the leading causes of mortality and disability worldwide, and their effective management is crucial to improving patients’ quality of life and reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
Characteristics of Chronic Diseases
Long duration: They persist for years or a lifetime.
Slow progression: They do not usually resolve spontaneously.
Multifactorial: Influenced by genetic, environmental, behavioral, and social factors.
Non-communicable: They are not contagious, although some may have infectious components (example: liver cancer due to viral hepatitis).
Impact on quality of life: They can limit functionality and require lifestyle adjustments.
Examples of Chronic Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases: High blood pressure, ischemic heart disease, heart failure.
Diabetes mellitus: Type 1 and type 2.
Chronic respiratory diseases: Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Cancer: Different types, such as breast, prostate, or lung cancer.
Neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s.
Autoimmune diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus.
Obesity: Considered a chronic disease due to its impact on health.